Foundations of Project Management
| 13 minutesUnderstanding Project Management
Let’s review general concepts to start understanding more about project management:
Becoming an effective project manager
Usually a Project Manager manages the project from start to finish and serves as a guide for their team, using their organizational and interpersonal skills every step of the way. Key values would be the prioritization (effectiveness to prioritize tasks), delegation (matching tasks to best individuals) and effective communication (both with team and stakeholders).
Remembering that Stakeholders are interested people and affected by the project’s completion and success. The leader of the organization could become a stakeholder as well.
Project Manager Responsibilities: Organizing product documentation, making use of productivity tools, creating schedules, managing tasks, budgeting, managing quality, and controlling costs.
Project Manager Skills:
Project Life Cycle and Methodologies
Phases in the Project Life Cycle refers to:
All these phases are part of any project in general, independent of the applied methodology.
Types of the Project Management Methodology that are mostly used in projects are linear and iterative:
Popular Project Management Approaches: currently most of the popular methodologies are waterfall and agile. However, there is a list of other project management methodologies that would be used depending on the nature of the project, project management knowledge, etc.:
In AdvaCare, currently we are applying an Agile (and even Scrum) approach across company projects. We also utilize elements of the Waterfall methodology.
Usually, the best time to implement Lean project management is when you want to use limited resources, reduce waste, and streamline processes to gain maximum benefits. Some scenarios where it would be required to reduce waste are: lack of proper documentation, lack of process standards, not understanding the customers’ needs, lack of effective communication, lack of process control, inefficient process design, failures of management, etc.
It can be achieved by using the pillars of the Lean 5S quality tool. The term 5S refers to the 5 pillars that are required for good housekeeping: sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain. The 5S method. Lean uses Kanban, a scheduling system to manage production. It enables to optimize the flow of team’s work, visual display to identify what needs to be done and when. Kanban and 5S are core principles of Lean Methodology.
Usually, the best time to implement Six Sigma is to find aspects of the product or process that are measurable like time, cost, or quantity. Then inspect that measurable item and reject any products that do not meet the Six Sigma standard. Any process that created unacceptable products has to be improved upon.
Two methodologies Lean + Six Sigma. The 5 phases on The Lean Six Sigma approach: define: project goal, similar to initiation phase, measure: focus on data, set a plan to how to get data and how to measure it, analyze: identify gaps and issues, improve: present your finding and get ready to start making improvements, control: learning from the work you did up front to put new processes and documentation in place (DMAIC). It's a strategy for process improvement, identifying where problems are in the current process and fixing them.
Examples:
Waterfall and Agile Comparison
|
|
Waterfall |
Agile |
|
Project Manager's Role |
Project manager serves as an active leader by prioritizing and assigning tasks to team members. |
Agile project manager (or Scrum Master) acts primarily as a facilitator, removing any barriers the team faces. Team shares more responsibility in managing their own work. |
|
Scope |
Project deliverables and plans are well-established and documented in the early stages of initiating and planning. Changes go through a formal change request process. |
Planning happens in shorter iterations and focuses on delivering value quickly. Subsequent iterations are adjusted in response to feedback or unforeseen issues. |
|
Schedule |
Follows a mostly linear path through the initiating, planning, executing, and closing phases of the project. |
Time is organized into phases called Sprints. Each Sprint has a defined duration, with a set list of deliverables planned at the start of the Sprint. |
|
Cost |
Costs are kept under control by careful estimation up front and close monitoring throughout the life cycle of the project. |
Costs and schedules could change with each iteration. |
|
Quality |
Project manager makes plans and clearly defines criteria to measure quality at the beginning of the project. |
Team solicits ongoing stakeholder input and user feedback by testing products in the field and regularly implementing improvements. |
|
Communication |
Project manager continually communicates progress toward milestones and other key indicators to stakeholders, ensuring that the project is on track to meet the customer’s expectations. |
Team is customer-focused, with consistent communication between users and the project team. |
|
Stakeholders |
Project manager continually manages and monitors stakeholder engagement to ensure the project is on track. |
Team frequently provides deliverables to stakeholders throughout the project. Progress toward milestones is dependent upon stakeholder feedback. |
Organizational Structure and Culture
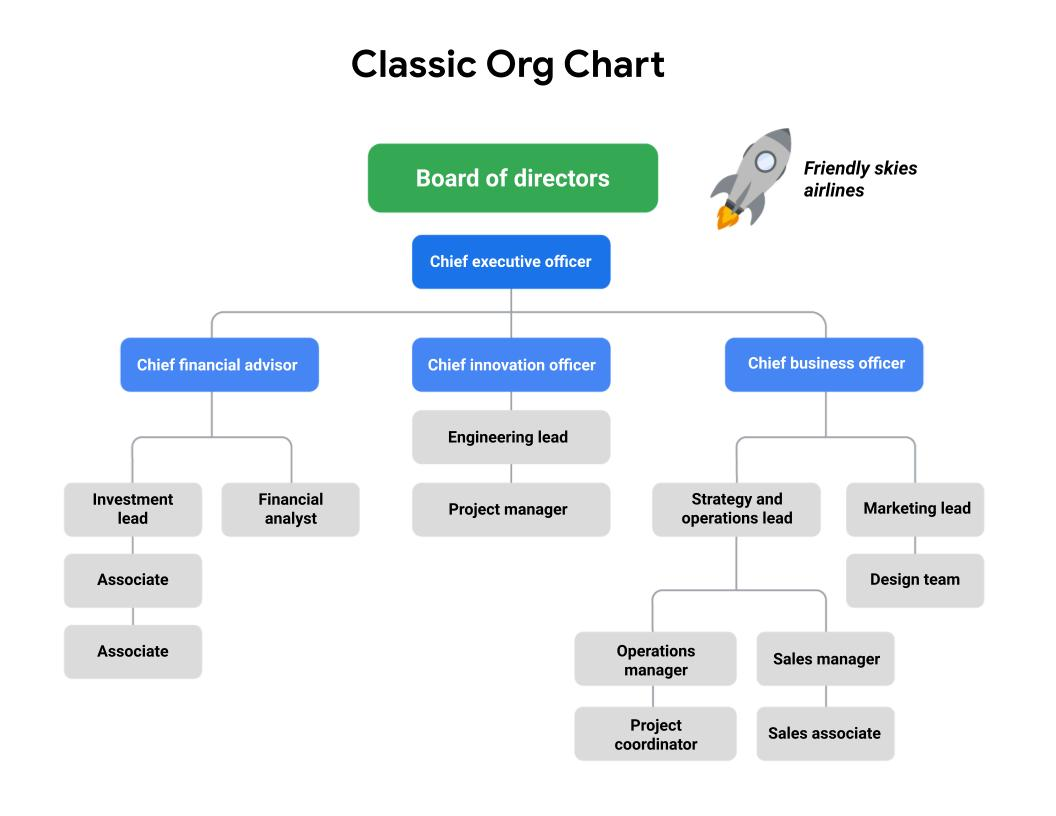
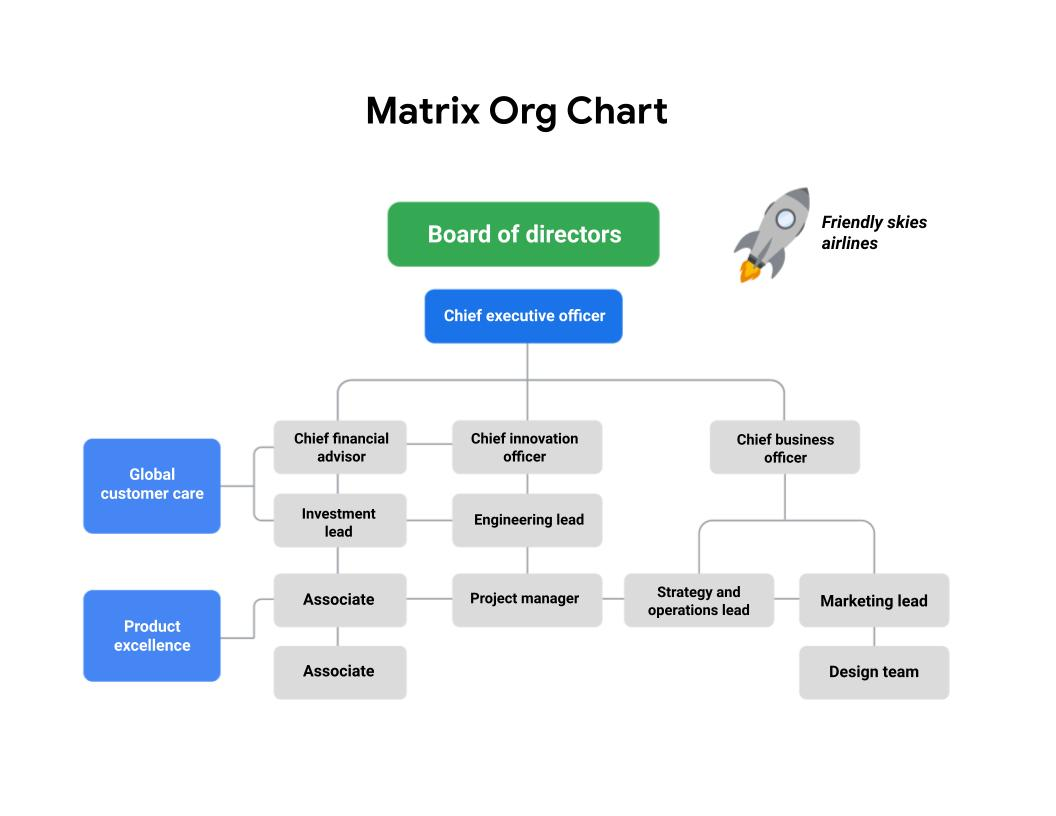
PMO is a team of project managers, coordinates different parts of a project. Critical thing is that a Project manager must have a bird’s eye view of everything that’s happening in a project. Biggest benefit is that we need to share a lot of best practices with each other.
By considering the long-term and short-term interests of the organization. By making thoughtful decisions about which projects to take on and avoiding projects if they don’t have sufficient resources. By providing stakeholders with timely, relevant, and reliable information.