Conducting Sprint Planning Session
| 16 minutesGeneral
To successfully conduct a Sprint planning meeting, it’s important to know prior general basic concepts of Agile Methodologies .
What is Sprint Planning?
Sprint planning is an event in Scrum (a type of Agile framework) that kicks off the Sprint session. This session immediately follows the Grooming session in which the project manager carefully plans the Sprint session. While Grooming can be thought of as the preparation stage, Sprint is the action, or implementation, stage. The purpose of Sprint planning is to define what can be delivered by the end of the Sprint session and how that work will be achieved.
Who participates?
Sprint planning is done in collaboration with the whole scrum team, or in the case of our company, all of the participants of a department or project. The Sprint meeting during which the deliverables for each participant, and the department or team as a whole, is led by a project manager.
Rather than simply being appointed or assigned tasks to be completed, the participants are encouraged to share relevant information that might affect the planning of the work to be completed during the Sprint session. The time allocated to every participant for each task or activity is estimated by the project manager, but is also an agreement with the participant that the allotted time is sufficient for each task/activity. At the close of the meeting, the participant is responsible to fulfill the tasks/activities as the time allocated was mutually agreed upon and determined to be sufficient.
What is the goal?
The primary goal of the Sprint meeting is to refine the tasks/activities planned during Grooming and kick-off what each participant is to do by the end of the Sprint session. In other words, it is a structured, well-organized kick-off meeting. Meanwhile, the primary goal of the Sprint session is to implement and execute the planned work and reach a greater goal of the entire department or team. Sprint meetings and sessions serve to organize all participants to reach common goals that result in greater efficiency, accuracy and ultimately, results.
Before leaping into action, it’s important to set up the Sprint. It’s required to decide on how long the time box is going to be, the Sprint goal, and where you're going to start. The Sprint planning session kicks off the Sprint by setting the agenda and focus. If done correctly, it also creates an environment where the team is motivated, challenged, and can be successful.
Sprint Meeting & Session Duration
The leader of the session is responsible for timeboxing the Sprint Planning meeting. Setting a time limit will encourage the team to stay focused.
How much time should you dedicate to a Sprint meeting?
The meeting duration should be under 60 minutes, and not to exceed 75 minutes.
However, the time required for a Sprint meeting can vary according to the number of stakeholders and time period of the Sprint session:
Overall, the goal should be to have a productive and focused refinement meeting. That said, excessive amounts of time cannot be spent on these sessions.
What is the frequency/duration of a Sprint Iteration (time-box)?
The duration of a Sprint Iteration (time-box), on an ongoing basis, should be according to the needs of the department, team or project. It is possible that the duration can be adjusted so to remain flexible and adaptive, but a set schedule brings the best results. In our company, the following schedule applies:
Efficiency is key with Sprint meetings. The project manager needs to keep things moving along and ensure conversations stay on track. It is at their discretion if to assign time limits for each participant to keep things moving. It might seem like there is a lot of work being squeezed into a short block of time, but if properly prepared there can easily be effective sessions.
Quickview: Getting Started
Who runs the Sprint sessions?
Department manager or Project manager. Further referred to as “project manager” in this SOP.
What is “Backlog Grooming”?
A session during which the project manager prepares for the upcoming Sprint session. The Grooming session is conducted right before the Sprint meeting so that the most recent status of work can be assessed to properly plan for the Sprint session.
What is the difference between a “Stakeholder” and “Owner”?
Owner (sometimes referred to just as Task Owner) is the participant in a Sprint session who is responsible for a task or sub-task, in essence the project manager of that specific task or sub-task. Stakeholder is the person in a Sprint session who partakes in a task or sub-task to bring it to completion.
*An Owner can become a Stakeholder, and visa versa.
What is a “Sprint Task Description”?
A list that summarizes the tasks for every participant in a Sprint session.
What are “Sprint Tasks in Kanban”?
A filtered Kanban showing every stage of Agile with all of the tasks and sub-tasks assigned to a specific participant of a Sprint session.
What is a “Projects Overview”?
A filtered Kanban showing every Project in ERP with the stages and all of the tasks and sub-tasks under a specific Project.
Conducting the Sprint Session
There are 3 main tools used to conduct Sprint sessions:
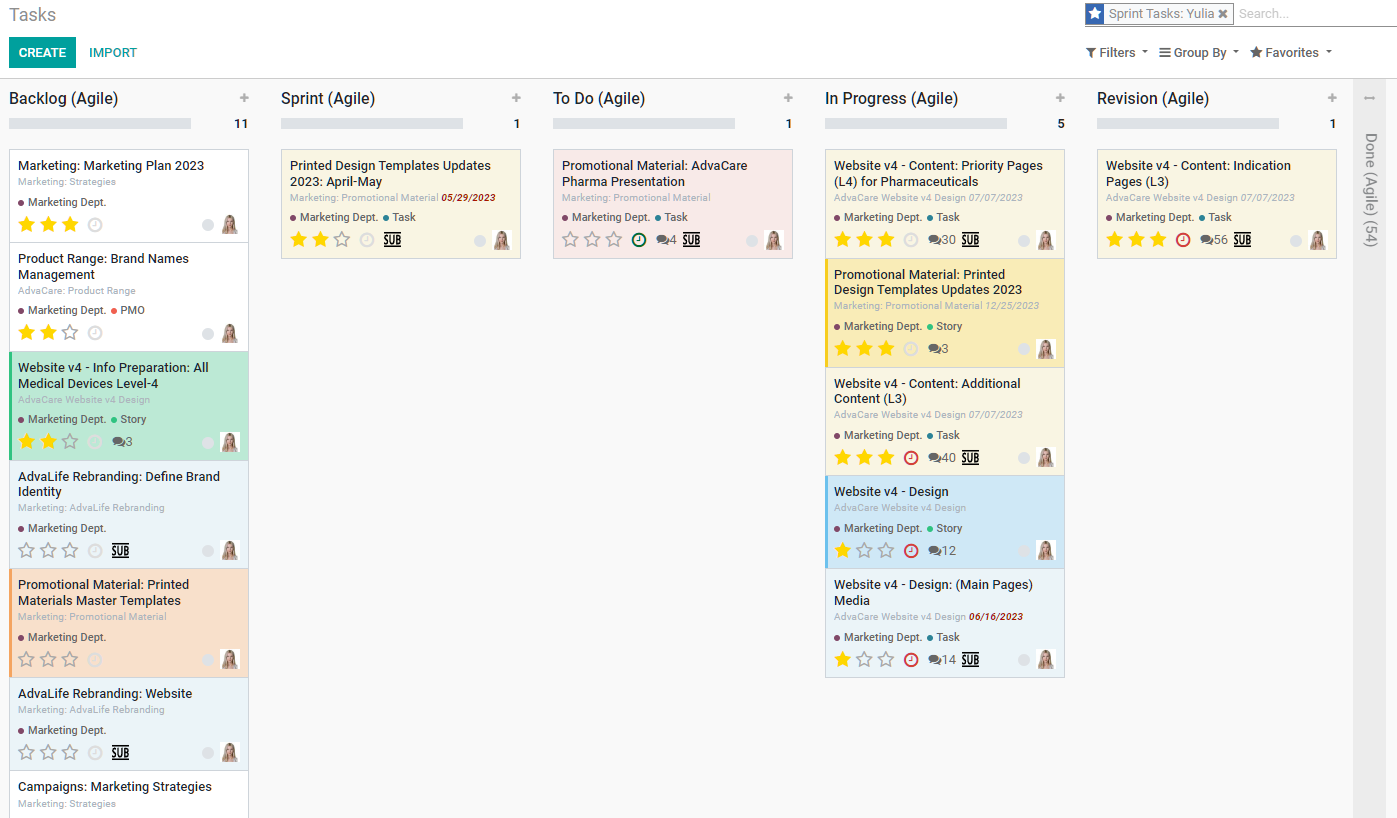
Backlog > Sprint > To Do > In Progress > Revision > Done
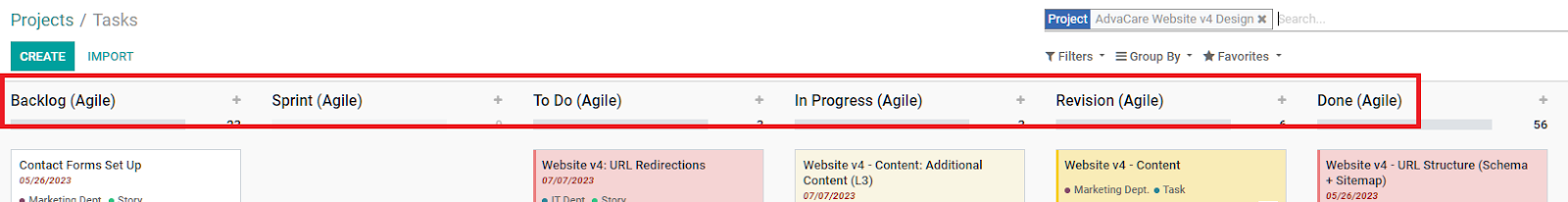
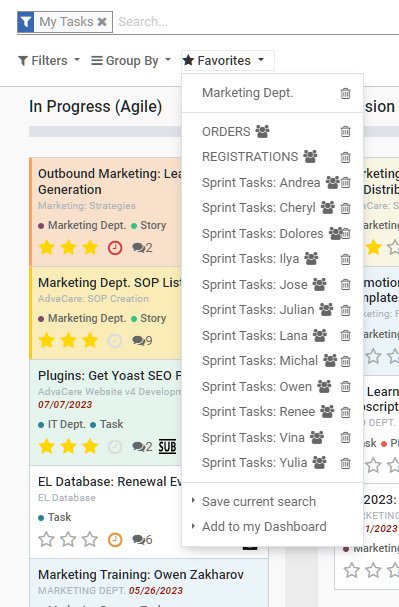
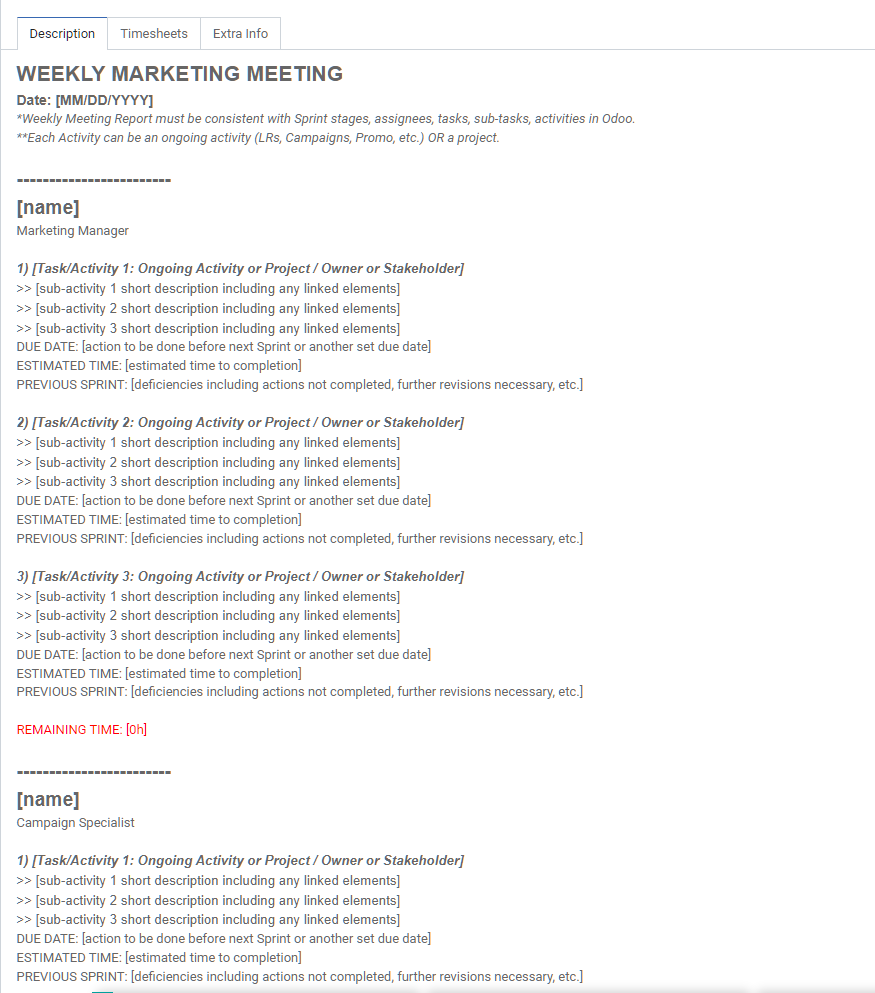
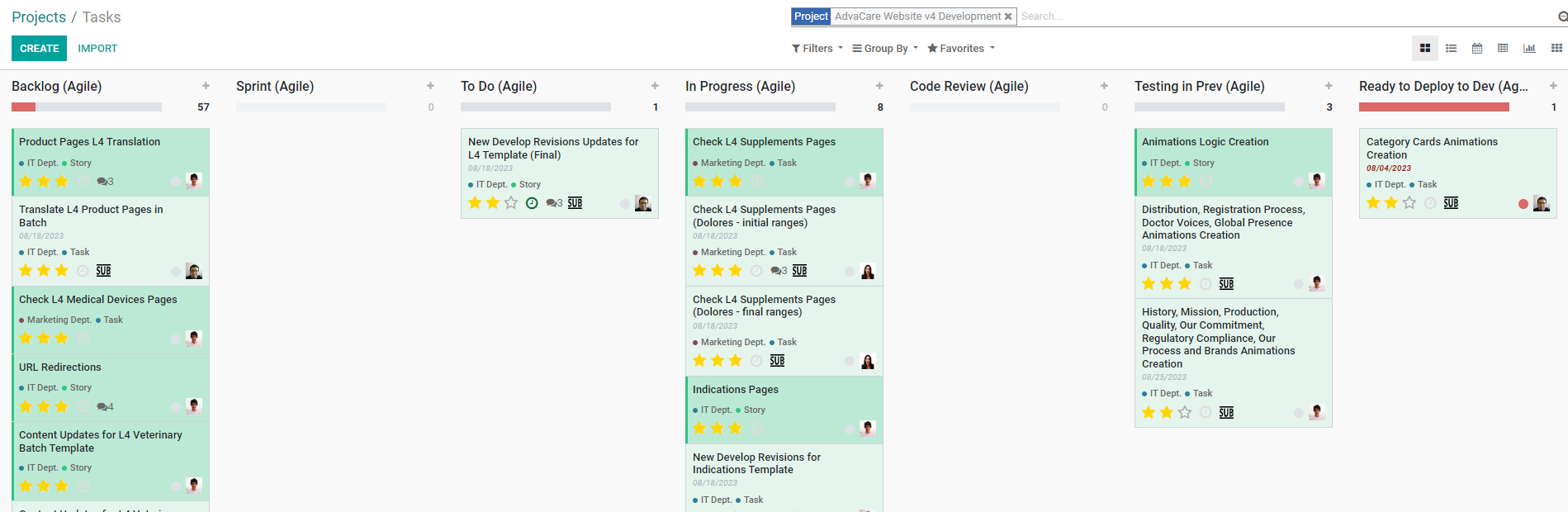
All the tools, the Sprint Task Description, Sprint Tasks Kanban and Projects Overview, are prepared by the project manager during the Grooming session prior to the Sprint session.
Step 1: Before Sprint Meeting
Before conducting the Sprint meeting, project manager reviews the previous Sprint Task Description task chatter to ensure that the most recent status updates of every stakeholder/owner have been received and considered in the Sprint Task Description.
Step 2: Conducting Sprint Meeting
The Sprint meeting is the most important event of the Sprint session as the responsibilities of every stakeholder/owner and the goals of the department/team are aligned for the Sprint session in this meeting. As the project manager goes through the Sprint Task Description and Sprint Tasks in Kanban, the time spent with each stakeholder/owner is focused on that specific stakeholder/owner, but other stakeholders are free to speak as many of the tasks/activities are collaborative with multiple stakeholders.
OPENING REMARKS: 5-10 minutes
NEW PROJECTS OVERVIEW: 5-10 minutes
There are 2 main methods to conduct the further steps of the Sprint Planning session:
Both methods have the same main goal - discuss every task assigned to each stakeholder/owner and make sure it is clear what needs to be completed in the upcoming Sprint iteration. The project manager can decide which approach is more suitable for the department or specific projects, based on the amount and complexity of the projects. Sometimes it is more useful to look at the project progress overall with the help of Projects Overview, and sometimes it is enough to look at Sprint Tasks in Kanban of each stakeholder/owner when the project manager has a very clear understanding of each project's overall status.
METHOD 1: PROJECTS OVERVIEW
TASK PLANNING: 5-10 minutes / project
Beginning with project #1 of the department, project manager opens each Project in ERP and looks through the tasks in stages In Progress, To Do, Revision and Sprint. The progress of every task/sub-task under the Project is discussed as necessary. Each new task/sub-task in Sprint stage is explained by the project manager and adjusted if required based on any changes discussed, but changes should be minimized as project manager prepared the status of tasks/sub-tasks for each stakeholder/owner in the Grooming session:
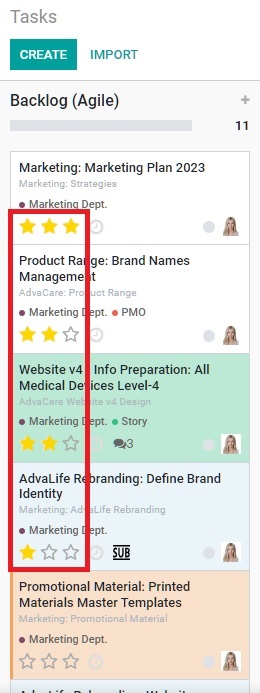
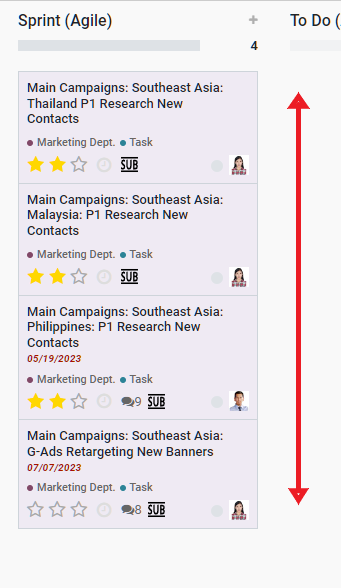
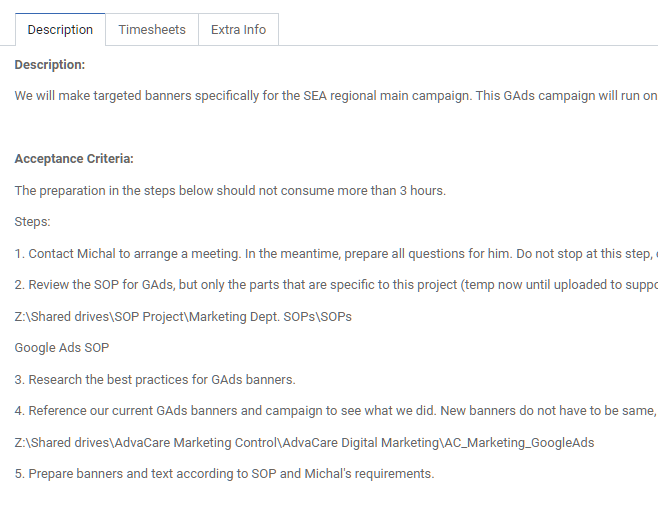
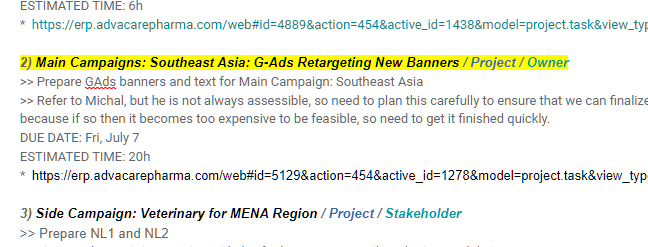
Any questions or adjustments to each specific itemized task/activity is to be handled as it is discussed. Specifically the ESTIMATED TIME should be confirmed by both the project manager and the stakeholder/owner.
Each task/activity should be clear and understood by the stakeholder/owner. The stakeholder/owner is responsible to fulfill each itemized task within the time allotment.
METHOD 2: SPRINT TASKS IN KANBAN
TASK PLANNING: 5-10 minutes / person
Beginning with stakeholder/owner #1 in the Sprint Task Description, project manager opens the Sprint Tasks in Kanban in ERP for that specific stakeholder/owner. The task/sub-task is adjusted if required based on any changes discussed, but changes should be minimized as project manager prepared the status of tasks/sub-tasks for each stakeholder/owner in the Grooming session:




Any questions or adjustments to each specific itemized task/activity is to be handled as it is discussed. Specifically the ESTIMATED TIME should be confirmed by both the project manager and the stakeholder/owner.
Each task/activity should be clear and understood by the stakeholder/owner. The stakeholder/owner is responsible to fulfill each itemized task within the time allotment.
Step 3: Stakeholder/Owner Responsibilities
After the Sprint meeting, the responsibility shifts to each stakeholder/owner in the Sprint to do the following for the tasks//sub-tasks to which he/she is assigned: